WordPress Terminology
Admin bar
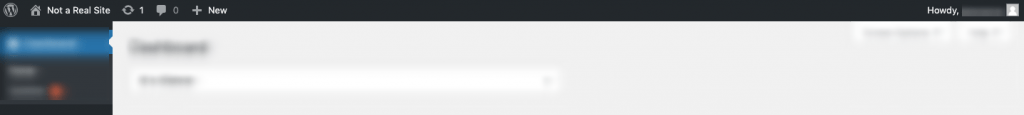 The admin bar is the sticky toolbar at the top of WordPress. It provides shortcut access to the live website, available updates, new comments, as well as quick-add capabilities for posts, pages, media and more. Users can also adjust the settings for their individual profiles from the top-right corner.
The admin bar is the sticky toolbar at the top of WordPress. It provides shortcut access to the live website, available updates, new comments, as well as quick-add capabilities for posts, pages, media and more. Users can also adjust the settings for their individual profiles from the top-right corner.
Autosave
When creating a new page or post, WordPress automatically saves a user’s progress every two minutes. At the end of the session, only the last version of the autosaved page remains. It’s the user’s responsibility to officially save changes to a work-in-progress with “Draft” or push them to the website with “Publish”.
Back end
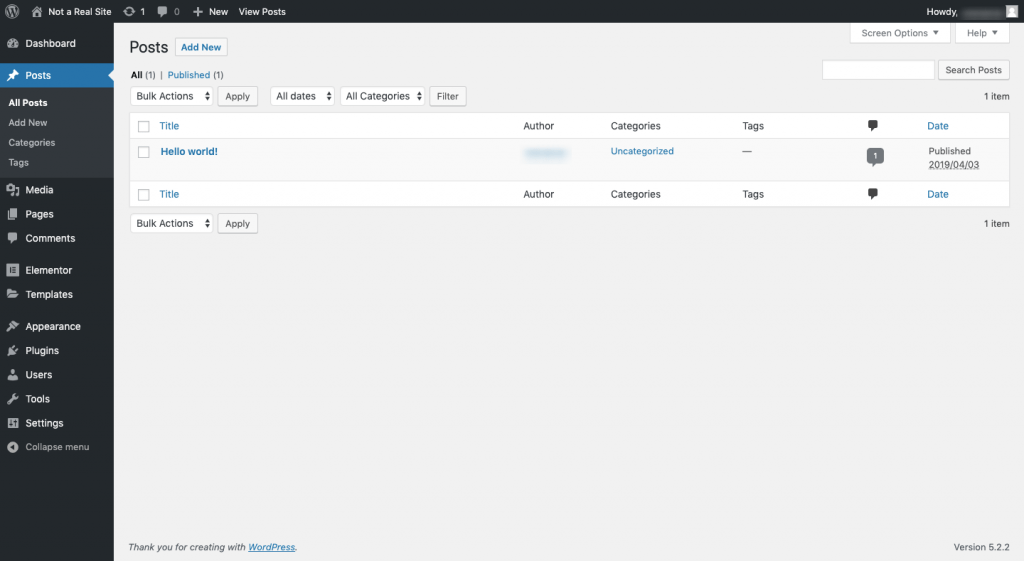 The back end of a WordPress website is anything found behind the scenes. For most users, this refers to the administration area where content is created, plugins are added and users are managed.
The back end of a WordPress website is anything found behind the scenes. For most users, this refers to the administration area where content is created, plugins are added and users are managed.
Block
The new WordPress editor uses blocks to build the smaller components of a page, from paragraphs of text to video players, and everything in between.
Block editor
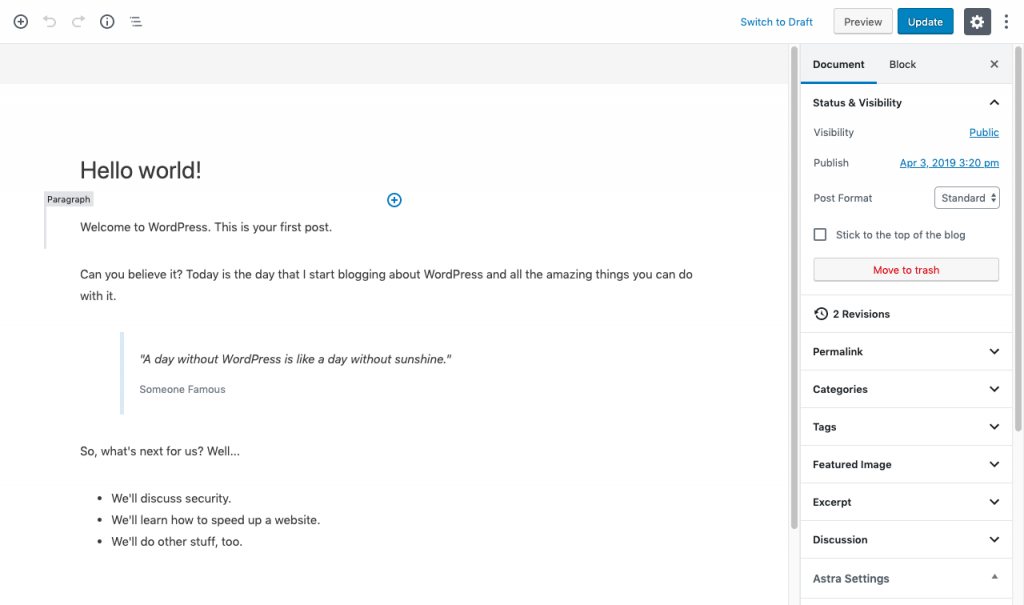 The WordPress editor, formerly known as “Gutenberg”, is a block-based page builder tool. Every component on the page is added with a dedicated block. Each block type comes with a unique toolbar to customise the styling of the element on the page.
The WordPress editor, formerly known as “Gutenberg”, is a block-based page builder tool. Every component on the page is added with a dedicated block. Each block type comes with a unique toolbar to customise the styling of the element on the page.
Blog
A blog is a place where content is written and published to a feed on a website. Businesses typically use blogs to share ideas, tutorials, case studies and other kinds of content. In WordPress, users create content for their blogs through the Posts screen.
Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs is a secondary navigation that usually appears in the top-left corner of a web page or post. Its job is to show users the trail they’ve followed on the website and make it easy for them to backtrack. For example:
Home > About Us > Staff Bios
Breadcrumbs may also be used to display how much progress a user has made in completing a form.
Category
A category is a type of taxonomy that’s applied to WordPress posts. Categories tend to be high-level topics that allow users to better organize their blog content.
Classic editor
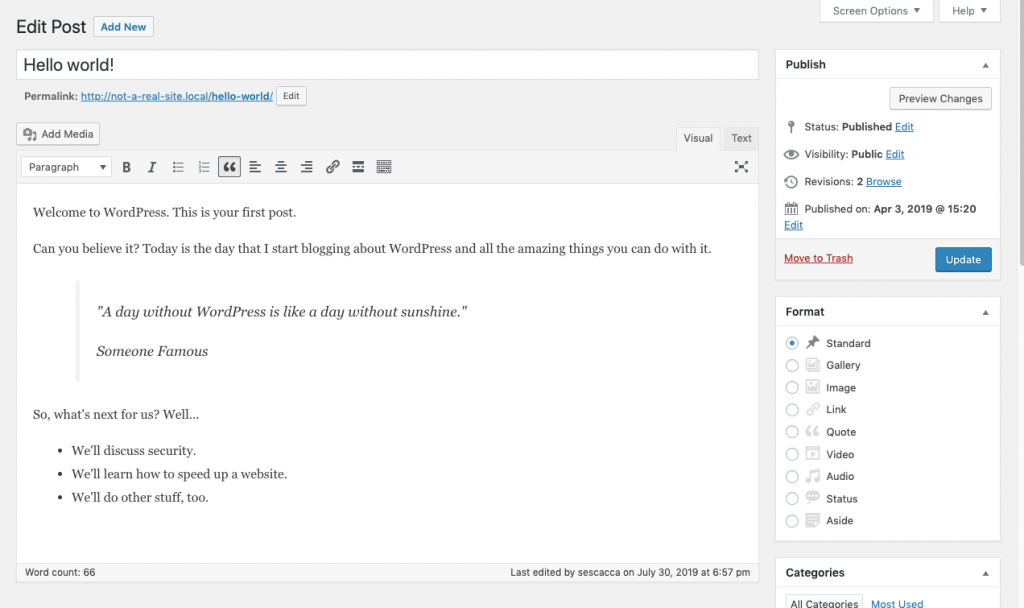 The classic editor was the default post and page editor for WordPress users prior to 2019. It included options for a visual and code editor.
The classic editor was the default post and page editor for WordPress users prior to 2019. It included options for a visual and code editor.
Users can revert to the classic editor with a plugin.
Code editor
The code editor in WordPress is the editing interface that lets users write and edit content with HTML.
Comment
A comment is a feature that can be turned on or off for the blog. This enables readers to submit comments to appear at the end of posts.
Content management system
A content management system (CMS) is a platform that enables users of all levels to create and publish websites on their own. WordPress is an example of a content management system.
Control panel
A control panel is an administration tool for web hosting and domain management, amongst other things. One of the most popular control panels is cPanel.
Front end
The front end of a WordPress website is the actual website visitors see when they go to your URL.
Gutenberg
Gutenberg was the name given to the new WordPress editor during its beta phase as a plugin.
HTML
HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language. This basic markup tells a web browser how to display content on a web page. It’s different from a programming language that creates very specific functionalities. HTML just makes it possible to arrange and format the text and images on the page, just as Microsoft Word does.
IP address
An IP address is a numerical identifier for both computers and web servers online. This is the ID web browsers use when retrieving a website for users. While each computer has a unique IP address, that’s not always the case for a web server that hosts multiple websites from a shared locale.
Media
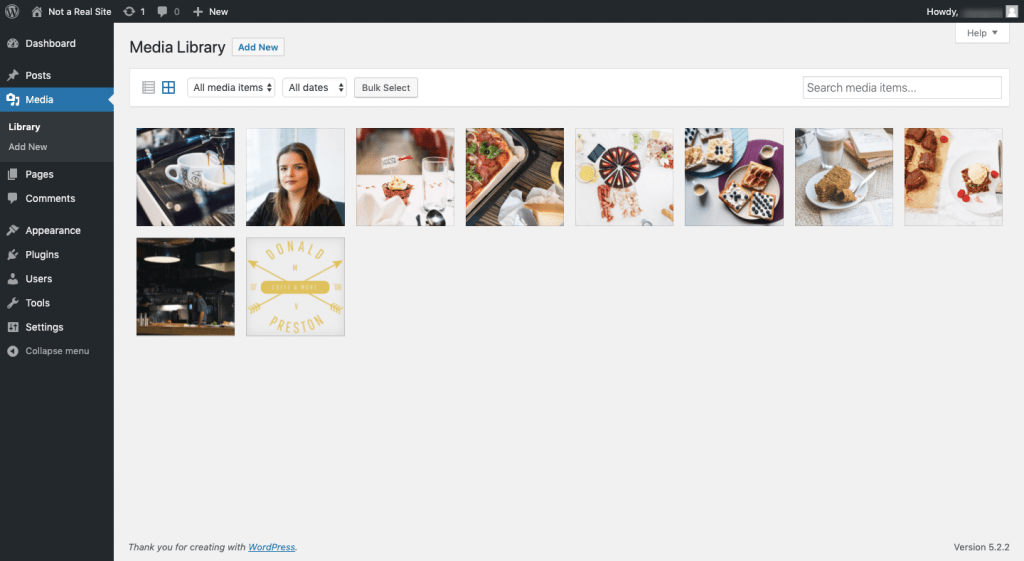 Media refers to the folder where files are uploaded to WordPress. Accepted file types include JPG images, PDF documents, MP3 audio clips and MP4 videos.
Media refers to the folder where files are uploaded to WordPress. Accepted file types include JPG images, PDF documents, MP3 audio clips and MP4 videos.
Menu
A menu is the list of pages that appear along the top of a website or stored beneath the hamburger icon on a mobile website.
MySQL
MySQL is a popular database management system used by hosting providers. It’s a highly organised structure that makes all data from a website easy to search for and manage.
Navigation
Navigation may sometimes be interchanged with a menu. However, it’s an all-encompassing term that includes any link on a website that directs visitors from one page to another.
Pages
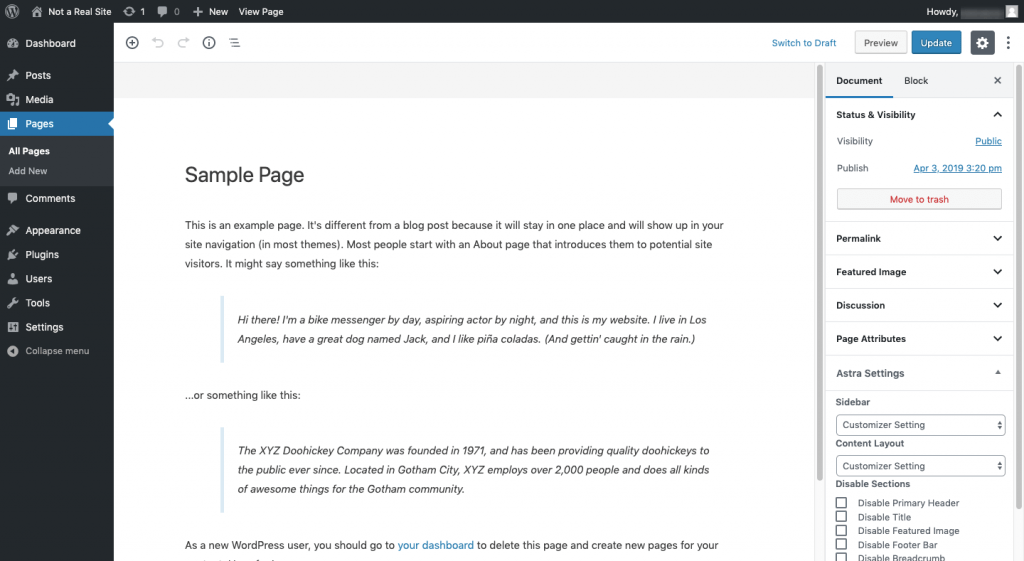
Any page on your website (published or unpublished) will be found in the “Pages” section of the backend. Here you can create a new page or edit an existing one. The only pages not found here are blog posts which can be found under “Posts” (see below).
Permalink
A permalink is a combination of the URL and slug and indicates where a specific page is found. WordPress gives users the option to simplify the structure of permalinks for easier visitor recall.
For example:
https://www.netelevation.com/knowledge-base
PHP
PHP is a server-side scripting and programming language. Developers use it to code the WordPress core, plugins and themes.
Plugin
A plugin is an add-on for WordPress that enables users to add new features or change functionality without having to use a single line of code.
Post
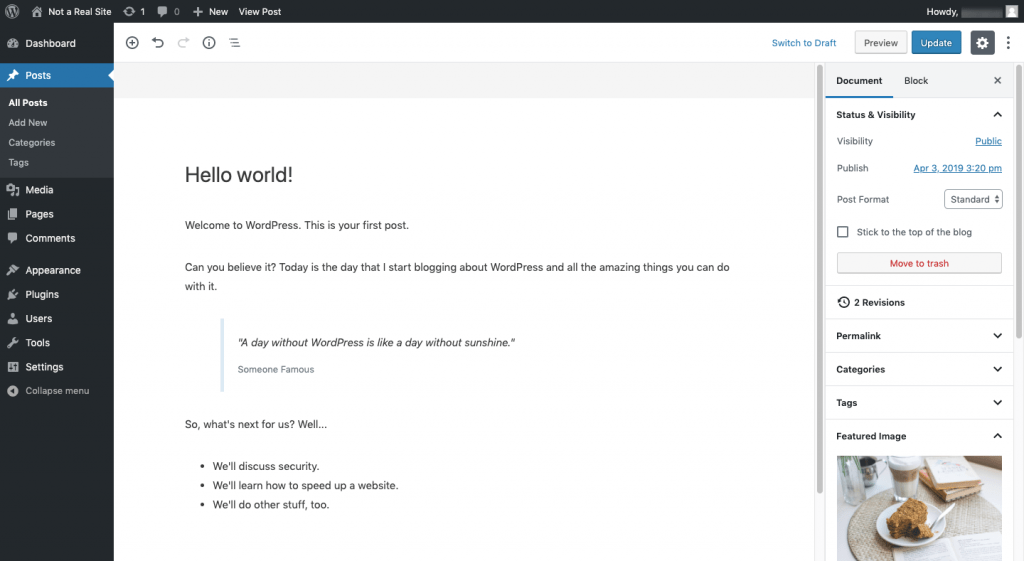 WordPress users create and manage the content for the blog or news section of their website with Posts.
WordPress users create and manage the content for the blog or news section of their website with Posts.
Post or page status
WordPress posts and pages can be saved in different ways.
“Draft” means it’s saved, but not published. “Published Public” means it’s on the website and able to be viewed by everyone. “Published Private” means only admins and editors logged into WordPress can view it. “Password Protected” means it’s published, but can only be viewed by people who have the password.
Revision
Any time content is saved to WordPress, a new revision is created. WordPress users can view their version history to see changes as well as revert to previous versions. They can also set a limit on how many revisions WordPress stores at a time.
Shortcode
A shortcode is a type of embed. However, a shortcode is a string of PHP that lets WordPress users embed an interactive element into a web page, like a calendar scheduling tool or a contact form.
Tag
A tag is a type of taxonomy that can be applied to WordPress posts. Unlike categories which are used for high-level organisation, tags work similarly to keywords. Multiple tags may be assigned to one post and sum up the lower-level topics covered within it.
Update
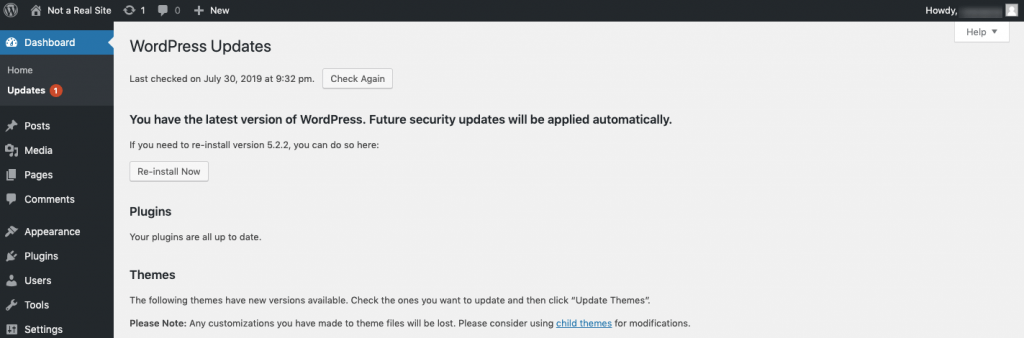 In WordPress, an update refers to code that has been changed or patched by the developer of the WordPress core, or a plugin or theme. When updates become available, WordPress alerts users with a notification and allows for one-click update privileges so that no coding or installation is needed.
In WordPress, an update refers to code that has been changed or patched by the developer of the WordPress core, or a plugin or theme. When updates become available, WordPress alerts users with a notification and allows for one-click update privileges so that no coding or installation is needed.
Upload
As opposed to embeds that use HTML to add external content to a website, uploads enable users to directly attach their Media to WordPress. These files then live and take up space on the website’s server.
User
A user is anyone who’s been granted access to WordPress. The admin can control what role the user plays (e.g. Editor, Subscriber, Contributor, etc.) as well as how much access they have to the various screens and view/edit controls in WordPress.
Visual editor
The visual editor in WordPress is the editing interface that allows users to write content in an interface that looks similar to how it will appear on the front end.
Widget
Widgets are small, self-contained blocks that users can place on their website. Depending on the structure and flexibility of the theme, widgets can be added to a number of spaces on a website. Most commonly, widgets appear in the footer and sidebar areas and may contain things like a list of recently published posts or a newsletter subscriber form.


 MADE IN THE USA
MADE IN THE USA